Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Resting Potential, Neurons, Nerve Fibres, Synaptic Knob, Neurotransmitters, Nerve Impulse, Generation of Nerve Impulse, Conduction of Nerve Impulse, and Transmission of Impulse at a Synapse.
Important Questions on Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
Two neurons, and , synapse onto a third neuron, . If neurotransmitter from A opens ligand-gated channels permeable to and and neurotransmitter from opens ligand-gated channels, which of the following statements is true?
During generation of an action potential, depolarisation is due to:
Resting membrane potential of a neuron is approximately:
Once a synaptic junction between neurons has allowed transmission of a nerve impulse, it is made ready to transmit next impulse by the action of:
Which of these fibres release epinephrine?
In nerve impulse conduction, the repolarization occurs with the
What happens during repolarization of nerve?
In the given figure two regions and of a neuron are shown. Out of the following, which option tells us best the state of the neuron at the two sites and the direction of flow of nerve impulse?
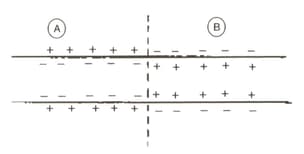
The Na-pump stops operating during:
What maintains the resting membrane potential?
Which one of the following pairs of structures differentiates a nerve cell from other types of cell?
The branch of Zoology dealing with the study of growing old is called
Digitalis is a drug that blocks the ase and causes which of the following consequences?
The neural membrane in the resting state, diffusion due to concentration gradients, allowed, would drive
The action potential is
Potential difference across resting membrane is negatively charged. This is due to the differential distribution of the following ions
When does the relative refractory period occur?
Resting membrane potential is maintained by
In a nerve cell potassium concentration is
Fill in the blanks by choosing the most suitable option:
A resting axonal membrane is comparatively more permeable to ........... and nearly impermeable to.......
